Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Tamura, Kazuhisa; Oko, Yoshihisa*; Tatsuma, Tetsu*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
We measured a cyclic voltammogram of TiO under intermittent X-ray irradiation and time courses of the rest potential under X-ray irradiation and in the dark. Both the oxidation current and the negative shift of the rest potential were observed only under irradiation, indicating that the electron-hole pair formation and the photocatalytic reaction occur under X-ray irradiation. We also measured action spectra of the photocurrent and photopotential. It was found that both the photocurrent and photopotential with very high quantum efficiency (400%) were observed above Ti-K edge and the fine structure of action spectra had the same structure of XANES spectrum, indicating that electrons in the valence band are excited during the relaxation process of excited inner shell electrons of Ti.
under intermittent X-ray irradiation and time courses of the rest potential under X-ray irradiation and in the dark. Both the oxidation current and the negative shift of the rest potential were observed only under irradiation, indicating that the electron-hole pair formation and the photocatalytic reaction occur under X-ray irradiation. We also measured action spectra of the photocurrent and photopotential. It was found that both the photocurrent and photopotential with very high quantum efficiency (400%) were observed above Ti-K edge and the fine structure of action spectra had the same structure of XANES spectrum, indicating that electrons in the valence band are excited during the relaxation process of excited inner shell electrons of Ti.
Seko, Noriaki; Kasai, Noboru; Hoshina, Hiroyuki*; Tamada, Masao; Ichikawa, Eiichi*
no journal, ,
Adsorption method is attractive to collect the metal from the seawater and the ground water without any slag from the viewpoint of security of metal resources and environmental preservation. In this method, the adsorbent needs the high selectivity and capacity for metal adsorption from the solution. We found that the rare metals such as a scandium were solved in the hot spring water. The temperature of hot spring water is feasible for metal adsorption by means of the graft adsorbent. Noble adsorbent is necessary for collecting the scandium from hot spring water since pH of the hot spring water is less than 2. We have synthesized a fibrous phosphoric adsorbent for recovery of scandium by using graft technique. The phosphoric adsorbent has high performance for scandium even in highly acidic condition when the phosphoric adsorbent was dipped into the 100ppb scandium solution it was found that 99% of scandium ions could be adsorbed within 2 hours. Removal of toxic metals from streaming water and the groundwater is also important task to preserve environment. Hot spring water contains toxic metals such as arsenic. The arsenic adsorbent was synthesized by loading zirconium on the phosphoric adsorbent. The resulting adsorbent had 100 times faster rate of arsenic adsorption than that of commercial resin. Furthermore, the zirconium loading phosphoric adsorbent could be adapted to the removal of arsenic from the hot spring water. This adsorbent adsorbed 1g-arsenic/kg-adsorbent for 1 week soaking in hot spring.
Kimura, Takaumi; Kirishima, Akira*; Arisaka, Makoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Nath, K. G.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -
- (e) spectroscopy of
(e) spectroscopy of  Rf and
Rf and  No
NoAsai, Masato
no journal, ,
 -
- and
and  -electron coincidence spectroscopy for the
-electron coincidence spectroscopy for the  decay of
decay of  Rf and
Rf and  No has been performed to study shell structure of superheavy nuclei through experimental spin-parity assignments. The neutron single-particle configuration of 3/2[622] has been assigned to the ground state of
No has been performed to study shell structure of superheavy nuclei through experimental spin-parity assignments. The neutron single-particle configuration of 3/2[622] has been assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 124.1 keV level in
No as well as to the 124.1 keV level in 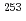 Fm. It was found that the ground state configuration of
Fm. It was found that the ground state configuration of  No is different from that of lighter N=155 isotones. The ground state configuration of
No is different from that of lighter N=155 isotones. The ground state configuration of  Rf is also discussed on the basis of the
Rf is also discussed on the basis of the  -
- coincidence results for
coincidence results for  Rf.
Rf.
Nagame, Yuichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Wasikiewicz, J. M.; Yagi, Toshiaki; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
In the past few decades a great interest has been focused on the research of naturally occurring polymers, so called polysaccharides. Their main advantages are occurrence in large amounts in nature, as well as their biodegradability. The chemically modified, water-soluble polysaccharide derivatives such as carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), carboxymethylstarch (CMS), carboxymethylchitin (CMCT) and carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS) have been widely used in many industrial applications such as food and medicine fields. The effect of ionizing radiation on aqueous solution of these polysaccharides leads to their degradations. However, the  -rays and the electron beam induced the intermolecular crosslinking in the paste-like conditions, i.e., concentration of 10-60%. When the concentration of these polymers was 20%, the gel fractions of CMC, CMS, CMCT and CMCS were 38, 54, 8, 0% at a dose of 20 kGy, respectively while that of CMCS was 40% at high dose of 100 kGy. The obtained biodegradable hydrogels swelled significantly up to about 500 times of dried gel in aqueous media. Radiation parameters of irradiation, such as yields of degradation and crosslinking and the gelation dose, were evaluated by sol-gel analysis on the basis of Charlesby-Rosiak equation. From comparison of the results, we concluded that the structure of functional groups as hydroxyl, carboxymethyl, amino and N-acetylamino groups and molecular weight of polymers are the most important factors for radiation crosslinking of polysaccharide derivatives. If the material has the branched chain structure with carboxymethyl group and high molecular weight, it was crosslinked easily by radiation. The great advantage of these hydrogels is that they might be biodegraded after utilization. The biodegradable hydrogel polymers, synthesized by radiation crosslinking were applied as pressure dispersion materials in the bedsore-prevention mat and water-adsorbent materials for the composting of the livestock excreta.
-rays and the electron beam induced the intermolecular crosslinking in the paste-like conditions, i.e., concentration of 10-60%. When the concentration of these polymers was 20%, the gel fractions of CMC, CMS, CMCT and CMCS were 38, 54, 8, 0% at a dose of 20 kGy, respectively while that of CMCS was 40% at high dose of 100 kGy. The obtained biodegradable hydrogels swelled significantly up to about 500 times of dried gel in aqueous media. Radiation parameters of irradiation, such as yields of degradation and crosslinking and the gelation dose, were evaluated by sol-gel analysis on the basis of Charlesby-Rosiak equation. From comparison of the results, we concluded that the structure of functional groups as hydroxyl, carboxymethyl, amino and N-acetylamino groups and molecular weight of polymers are the most important factors for radiation crosslinking of polysaccharide derivatives. If the material has the branched chain structure with carboxymethyl group and high molecular weight, it was crosslinked easily by radiation. The great advantage of these hydrogels is that they might be biodegraded after utilization. The biodegradable hydrogel polymers, synthesized by radiation crosslinking were applied as pressure dispersion materials in the bedsore-prevention mat and water-adsorbent materials for the composting of the livestock excreta.
Kozai, Naofumi; Ozaki, Takuo; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Nankawa, Takuya; Sakai, Takuro; Francis, A. J.*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ozaki, Takuo; Kimura, Takaumi; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.*
no journal, ,
Elucidation of the coordination structure of radionuclides on microbial cells is necessary to precisely predict the effect of microorganisms on the environmental behavior of radionuclides. In this study, the association of f-elements, Eu(III) and Cm(III) with 13 kinds of microorganisms was examined by a batch method and time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (TRLFS). All the microorganisms used showed rapid kinetics and high distribution ratios of Eu(III) and Cm(III) on the cell surfaces. However, characteristics of the coordination environment of Eu(III) on the microorganisms significantly differed to each other: halophiles (4 strains) provided stronger ligand fields for Eu(III) compared to those non-halophiles (9 strains) did. These findings suggest that trivalent f-elements on the cells of halophiles are retained more tightly than those on non-halophiles.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji; Hatano, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Zenko
no journal, ,
Radiation-induced reduction of chromium(VI) ion in aqueous solution was investigated in the presence of small amount of insoluble oxide particle such as TiO , Al
, Al O
O and SiO
and SiO by using
by using  Co
Co  -ray. Solution at pH
-ray. Solution at pH  1.0, simulating industrial liquid waste, became neutral or basic by adding the oxide particle: the positive shift of pH of solution was dependent on the kind and particle size of oxide. The chromium(VI) ion was successfully reduced in the radiolysis of the neutral or basic solution in the presence of oxide, while not in the absence. These indicate that amount of chromium(VI) reduced by reducing radicals of water radiolysis is almost equal to that of chromium with the lower oxidation state oxidized by the oxidizing radicals in the solution, and that adsorption of chromium to oxide and enhancement in the reduction of chromium(VI) take place in the presence of oxide. The insoluble chromium(III) oxide formed in the reduction of chromium(VI) was also responsible for the reduction. The radiation-induced reduction process of hazardous chromium(VI) with utilizing high-level radioactive wastes as radiation resources was further discussed.
1.0, simulating industrial liquid waste, became neutral or basic by adding the oxide particle: the positive shift of pH of solution was dependent on the kind and particle size of oxide. The chromium(VI) ion was successfully reduced in the radiolysis of the neutral or basic solution in the presence of oxide, while not in the absence. These indicate that amount of chromium(VI) reduced by reducing radicals of water radiolysis is almost equal to that of chromium with the lower oxidation state oxidized by the oxidizing radicals in the solution, and that adsorption of chromium to oxide and enhancement in the reduction of chromium(VI) take place in the presence of oxide. The insoluble chromium(III) oxide formed in the reduction of chromium(VI) was also responsible for the reduction. The radiation-induced reduction process of hazardous chromium(VI) with utilizing high-level radioactive wastes as radiation resources was further discussed.
Ichikawa, Shinichi
no journal, ,
In accordance with the JAERI (Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute)-KEK (High Energy Accelerator Research Organization) collaborative research project, an ISOL-based radioactive ion beam facility, TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex), has been constructed at JAERI, Tokai. This facility consists of an Isotope Separator On-line (JAERI-ISOL) connected to the JAERI tandem accelerator, a charge-breeding 18 GHz ECR (CB-ECRIS) and split-coaxial RFQ and interdigital-H type linacs. Radioactive singly-charged ions from the JAERI-ISOL are bred to A/q  7 in the CB-ECRIS and then multi-charged ions are accelerated with the linac-complex from 2 keV/u to the energy between 0.1 to 1.1 MeV/u. So far, various kinds of neutron-rich radioactive nuclei produced in proton-induced fission of uranium have been ionized using the FEBIAD type ion source and mass-separated by the JAERI-ISOL. The charge-breeding efficiency of the CB-ECRIS was measured for stable Ar, Kr and Xe isotopes in a series of experiments. At March 2005, we successfully accelerated
7 in the CB-ECRIS and then multi-charged ions are accelerated with the linac-complex from 2 keV/u to the energy between 0.1 to 1.1 MeV/u. So far, various kinds of neutron-rich radioactive nuclei produced in proton-induced fission of uranium have been ionized using the FEBIAD type ion source and mass-separated by the JAERI-ISOL. The charge-breeding efficiency of the CB-ECRIS was measured for stable Ar, Kr and Xe isotopes in a series of experiments. At March 2005, we successfully accelerated 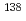 Xe produced in the proton-induced fission of uranium. The charge state of the accelerated
Xe produced in the proton-induced fission of uranium. The charge state of the accelerated 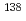 Xe was 20+ bred in-flight by the CB-ECRIS and acceleration energy of 1.1 MeV/u was achieved. In this conference, we will report the status of the TRIAC facility including the performance of the ISOL ion-source and the CB-ECRIS system as well as the future plan of this facility.
Xe was 20+ bred in-flight by the CB-ECRIS and acceleration energy of 1.1 MeV/u was achieved. In this conference, we will report the status of the TRIAC facility including the performance of the ISOL ion-source and the CB-ECRIS system as well as the future plan of this facility.
Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Yuji
no journal, ,
We have carried out systematic investigations of X-ray radiation properties of relativistic cluster plasmas created by the action of superintense laser irradiation. In order to demonstrate the practical capability of X-rays thus produced, the pulse X-ray diffraction is examined from Si(111) crystal with this source. We also report the generation of relativistic electron jet from cluster targets.